Web 3.0 represents the next major evolution of the internet, designed to create a smarter, more secure, and more user-controlled digital world. Unlike Web 2.0, where data is stored and controlled by large centralized companies, Web 3.0 aims to give power back to users through decentralization and advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain.
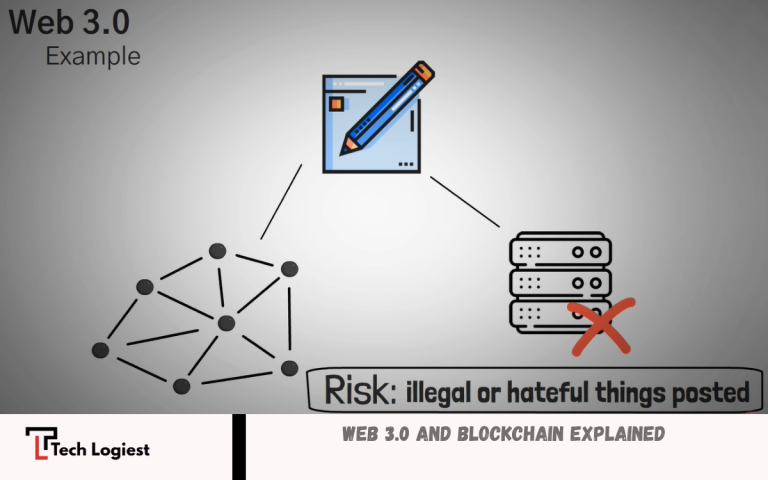
At the core of Web 3.0 is blockchain, a distributed ledger system that records data across a network of computers rather than on a single server. Because information is stored in blocks that are linked and secured using cryptography, it becomes nearly impossible to alter or manipulate.
The Evolution of the Internet: From Web 1.0 to Web 3.0
To understand Web 3.0, it’s important to know how the internet evolved.
Web 1.0 – The Static Internet (1990–2005)
Web 1.0 was the first version of the internet, simple, static, and mostly read-only. Websites were like digital brochures with text and images, and there was limited interaction. Users could visit pages, but could not create content easily.
Web 2.0 – The Social & Interactive Internet (2005–Present)
Web 2.0 brought dynamic websites, social networks, mobile apps, and user-generated content. Platforms like Facebook, YouTube, Instagram, Google, and Twitter became giants.
But there was a problem:
Huge tech companies gained control over user data, online identities, privacy, and monetization.
Web 2.0 is centralized. The platforms own the data, not the users.
Web 3.0 – The Decentralized, Intelligent Internet (Now & Future)
Web 3.0 is the next phase, aiming to fix Web 2.0’s weaknesses. It is defined by:
- Decentralization (powered by blockchain)
- User ownership of data
- Smart contracts instead of intermediaries
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning
- Personalized and trustless internet interactions
Web 3.0 is about giving control back to users, not corporations.
What Is Blockchain? The Foundation of Web 3.0
Blockchain is the technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, but its uses go far beyond digital money.
Blockchain in Simple Words
A blockchain is a digital ledger that records transactions across many computers in a network. Instead of being stored on a single server, data is spread across many nodes, making it:
- Transparent
- Secure
- Tamper-proof
- Decentralized
Each record is stored in a block, linked to the previous block—hence the name blockchain.
Why Blockchain Is Revolutionary
- No Single Authority Controls the Data
Unlike banks or companies, no one can secretly change records. - Highly Secure and Difficult to Hack
Data is locked using cryptography. - Transparency Builds Trust
Anyone can verify the information on a public blockchain. - Automated Transactions with Smart Contracts
Programs that run automatically when conditions are met no middleman needed.
Blockchain is the backbone of Web 3.0, supporting decentralized applications, digital currencies, and more.
Key Features of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is defined by several major characteristics:
1. Decentralization
Unlike Web 2.0, where platforms store data in centralized servers, Web 3.0 stores data on blockchain networks. This prevents misuse, censorship, or data manipulation.
2. Ownership of Data
Users control their identity, digital assets, and information.
For example, with Web 3.0 wallets like MetaMask, users hold their own keys.
3. Trustless Interactions
No need to rely on third parties like banks, payment processors, or intermediaries.
4. Token Economy
Web 3.0 introduces digital tokens and cryptocurrencies to reward participation and ownership.
5. Interoperability
Applications can communicate with each other without centralized APIs.
6. Artificial Intelligence & Semantic Understanding
Web 3.0 uses AI to understand content the same way humans do, making the internet more intuitive.
How Blockchain Powers Web 3.0
Blockchain and Web 3.0 are deeply connected.
1. Digital Identity (Self-Sovereign Identity)
Users can create identities without depending on platforms like Facebook or Google.
Your identity belongs to you.
2. Smart Contracts
Web 3.0 applications run on smart contracts instead of centralized servers.
These contracts automatically execute rules no human needed.
3. Decentralized Applications (dApps)
dApps run on blockchain and remain available even if servers go down or companies shut down.
Examples include:
- Uniswap (DeFi exchange)
- OpenSea (NFT marketplace)
- Aave (lending platform)
- Axie Infinity (game)
4. Decentralized Storage
Instead of storing files on centralized companies like Google Drive or Dropbox, Web 3.0 uses:
- IPFS
- Filecoin
- Arweave
This makes data permanent, censorship-resistant, and controlled by users.
Read Also: Latest Gadget Reviews – Features, Performance, and Value
Real-World Applications of Web 3.0 and Blockchain
1. Cryptocurrencies
Digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum allow people to send and receive payments globally without banks.
2. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi allows anyone to borrow, lend, trade, and earn interest without a bank.
3. NFTs (Digital Ownership)
NFTs represent ownership of digital assets like:
- Art
- Music
- In-game items
- Virtual land
NFTs gave birth to the creator economy without middlemen.
4. The Metaverse
A virtual world where users own assets through blockchain.
Web 3.0 metaverses include:
- Decentraland
- The Sandbox
5. Supply Chain Tracking
Blockchain ensures transparency across supply chains, showing where products come from.
6. Healthcare Data Security
Patients can control their medical records securely.
7. Voting Systems
Blockchain voting is transparent and tamper-proof.
Benefits of Web 3.0 and Blockchain
1. More Privacy and Security
Users have full control over their digital identities and data.
2. Censorship Resistance
No single company can control, restrict, or manipulate content.
3. Reduced Middlemen
Smart contracts automate processes and reduce costs.
4. Global Access
Anyone with internet can participate in Web 3.0 economies.
5. Better Monetization for Creators
Creators can earn directly through NFTs, tokens, and decentralized platforms.
Challenges and Limitations
1. Scalability Issues
Blockchains like Ethereum can become slow or expensive during high traffic.
2. Complex User Experience
Wallets, private keys, and transactions are difficult for beginners.
3. Regulations
Many governments are still adapting to crypto and blockchain laws.
4. Security Risks in Smart Contracts
Poor coding can lead to hacks or exploits.
5. Environmental Concerns
Some blockchains use high energy, though newer ones are more eco-friendly.
The Future of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is still evolving, but it promises a future where:
- Social media becomes user-owned
- Payments are instant, global, and low-cost
- Gaming integrates real asset ownership
- Artificial intelligence personalizes experiences
- Metaverse worlds become mainstream
- Decentralized apps dominate online activity
Major companies like Meta, Google, Apple, Microsoft, and Disney are already investing in blockchain and metaverse technologies, proving that Web 3.0 is not just a trend it’s the next chapter of the internet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Web 3.0 only about cryptocurrency?
No. While cryptocurrency is a major part, Web 3.0 also includes NFTs, decentralized apps (dApps), the metaverse, decentralized finance (DeFi), and more.
What are dApps?
Decentralized applications (dApps) are apps built on blockchain technology that run without centralized control, offering more transparency and security.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on the blockchain. They automatically perform actions when specific conditions are met no middleman required.
What are NFTs in Web 3.0?
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) represent ownership of unique digital assets like artwork, music, collectibles, or virtual land in the metaverse.
Is Web 3.0 safe?
Web 3.0 is generally more secure because of blockchain’s transparency and encryption, but users must still protect their wallets, private keys, and avoid scams.
What is DeFi?
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) refers to financial services built on blockchain such as lending, borrowing, trading, and earning rewards without banks or intermediaries.
When will Web 3.0 become mainstream?
Web 3.0 is growing rapidly, but adoption will increase as governments regulate crypto, companies build Web 3.0 apps, and user experience becomes easier.
Conclusion
Web 3.0 and blockchain represent a powerful shift toward a fairer, more transparent, and user-controlled internet. Blockchain’s decentralization, security, and transparency underpin innovations such as cryptocurrencies, NFTs, DeFi, decentralized apps, and metaverse worlds. While Web 3.0 still faces challenges like scalability and regulation, its potential to transform industries is enormous.
Web 3.0 promises a future where users not companies own their data, identities, and online experiences. Understanding these technologies today is essential for participating in the internet of tomorrow.